Cotton, with its inherent style, has been a constant thread in the narrative of human history. This natural fiber, which has gracefully dressed civilizations for millennia, stands as a testament to the enduring taste and preferences of humanity.
Beyond its soft touch and breathability lies its true power – versatility, making it an indispensable style icon in our daily wardrobes.
In this article, we’ll weave through the intricate tapestry of cotton’s history, explore the art and style of its cultivation, delve into its numerous uses, and discuss the contemporary environmental implications of this remarkable plant.
So, grab a comfortable cotton shirt, sit back, and let’s embark on this fascinating journey together!
Table of Contents
What is the Origin of Cotton?
The ancient relationship between humans and cotton spans over 7,000 years, finding roots in the civilizations of the Indus Valley, Egypt, and Mesoamerica.
These societies, though geographically distant, recognized cotton’s value and incorporated its cultivation and weaving into their daily lives.
By the medieval era, Europe, through its interactions with Arab traders and later through maritime routes to India and colonization of the Americas, embraced cotton.
This integration deepened during the Industrial Revolution, with innovations like Eli Whitney’s cotton gin in 1793, reinforcing cotton’s pivotal role in the global textile industry and economy.
How is Cotton made?
Cotton plants thrive in sunny, warm climates with moderate rainfall. They require a lengthy frost-free period for optimal growth. Key cotton-producing nations include China, India, the United States, Pakistan, and Brazil.
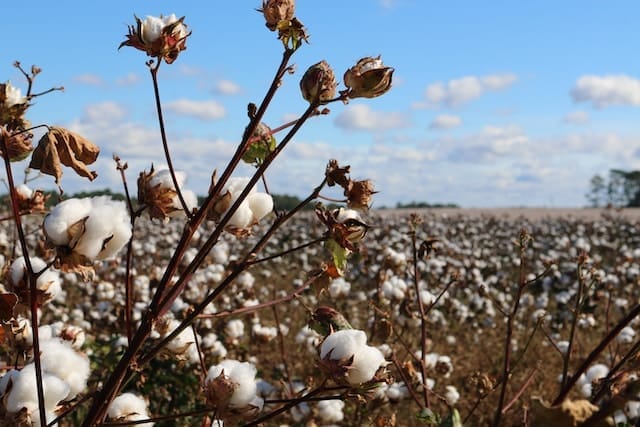

The plant produces cotton bolls, which contain the soft fibers that we associate with cotton clothing. Once these bolls mature, they are harvested. In modern times, machines often handle this task, though hand-picking remains common in some regions.
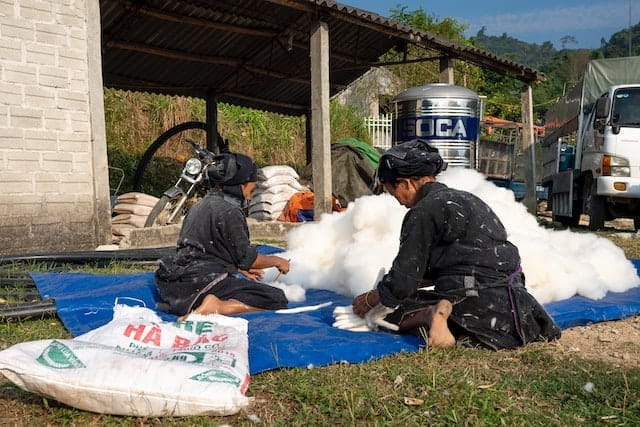

Post-harvest, cotton goes through a ginning process to separate the usable fibers from seeds. These fibers are then spun into yarns, which can be woven or knitted to produce fabrics.

Uses of Cotton
Cotton’s versatility has led to a plethora of applications, including:
Textiles
This is the most common use. From T-shirts, jeans, towels to high-end fashion garments, cotton’s presence is ubiquitous.
Medical Supplies
Cotton balls, bandages, and sanitary products are made from cotton due to its absorbency and softness.
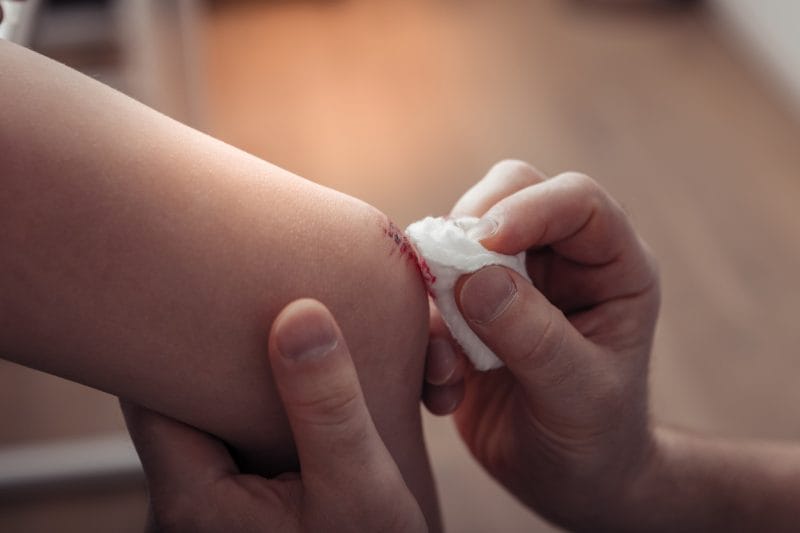
Industrial Uses
Cotton can be found in items like tents, fishnets, book bindings, and even in certain types of paper.
Cottonseed
A byproduct of cotton production, cottonseed can be processed to produce oil, which is used in foods and cosmetics.
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Cotton Production?
While cotton’s benefits are numerous, its cultivation has environmental implications:
Water Consumption
Cotton farming can be water-intensive. It’s estimated that producing a single cotton T-shirt can consume over 2,500 liters of water.

Pesticides and Chemicals
Cotton crops are notorious for their heavy use of pesticides and synthetic fertilizers, which can be detrimental to the environment and harmful to farmworkers.
Land Use
Expansive cotton farms can lead to deforestation and habitat destruction.
To combat these issues, there’s a growing demand for organic cotton, which is grown without synthetic chemicals, and sustainable farming practices are being promoted.
What Makes Cotton So Comfortable?
Cotton’s comfort lies in its natural properties.
The fibers are soft, breathable, and absorb moisture well, making cotton clothing comfortable to wear in a variety of climates.
Cotton also has a natural stretch, which allows garments to move with the body, adding to the overall comfort.
How Does Cotton Compare to Other Fabrics?
Compared to synthetic fibers like polyester, cotton is more breathable and often feels more pleasant against the skin. However, cotton does wrinkle more easily and may not be as durable as some synthetics.
Compared to other natural fibers like linen or wool, cotton is often softer and more versatile, being suitable for a wider range of garments and uses.
What Is the Future of Cotton?
The future of cotton lies in balancing its immense popularity and usefulness with the growing need for sustainable and environmentally friendly production practices.
Innovations in cotton farming, such as the development of drought-resistant cotton varieties and the use of precision agriculture techniques, offer hope for reducing cotton’s environmental footprint.
Simultaneously, the rise of organic cotton and the increasing consumer awareness about sustainable fashion point towards a future where cotton can continue to be a vital part of our lives while also being gentler on the planet.
Conclusion
In a world that is increasingly conscious of sustainability and environmental impact, cotton’s journey serves as a reminder of the delicate balance between progress and preservation. As the fabric of many civilizations, its versatility and adaptability have remained unmatched.
Yet, with the challenges posed by modern agriculture and industrialization, it’s incumbent upon both producers and consumers to champion eco-friendly practices.

The blend of tradition with innovation, heritage with responsibility, ensures that cotton not only maintains its revered position in global trade and culture but does so in harmony with the environment.
Harnessing new technologies and sustainable methods, we have the opportunity to write a new chapter for cotton, one that celebrates its rich history while also safeguarding our planet’s future.
So the next time you slip on your favorite cotton T-shirt or snuggle into your cozy cotton sheets, take a moment to appreciate the long, fascinating journey this humble fiber has taken to reach you.
From ancient civilizations to modern runways, cotton continues to weave its way into our hearts and our wardrobes, a timeless testament to its enduring appeal.
FAQs
Is cotton a natural or synthetic fiber?
Cotton is a natural fiber that comes from the cotton plant.
Which countries are the largest producers of cotton?
China and India are currently the largest producers of cotton worldwide.
How long does it take for a cotton plant to mature?
Cotton plants typically take about 5-6 months from planting to maturity.
Can cotton be recycled?
Yes, cotton can be recycled. Old cotton clothing can be repurposed into new garments, insulation, or even paper.
What is organic cotton?
Organic cotton is grown using methods and materials that have a low impact on the environment, without the use of synthetic pesticides or fertilizers.







Leave a Reply